Art Must Be Able to Convey a Message Theory Name
Every bit children, we spend time in schoolhouse learning about the basics of color. But few of us learn about the fundamentals of color theory.
Colour theory can exist a valuable tool to not only assistance united states understand more about the world around us but also to create harmonious designs (or decorate your home).
In this post, nosotros'll explain what colour theory is, why color theory matters, the different color models, and how you tin can more finer utilise color in your life.

What Is Color?
We spend and then much time around color that we often assume nosotros know what colour is without really thinking about its definition.
At its core, colour is perception. Our optics see something and the data sent from our eyes to our brains interprets it as a particular color.
Objects reflect low-cal in dissimilar combinations of wavelengths (radio, gamma rays, and more). Our brains choice up on these wavelength combinations, interpreting them as a miracle known as colour.
Color is the identify where our brain and the universe meet.
Paul Klee
What Is Colour Theory?
Color theory is the art and science of using color. It explains how humans perceive colour (both physically and psychologically) and how colors mix, match, and contrast with one some other.
It also factors in the messages that colors communicate.
On a more practical level, color theory also explains how specific colors can exist replicated in press, computers, art, and more – it'due south an overarching, multifaceted field.
At its simplest, color theory creates a logical structure to something we deal with every day but might not ever fully understand or take the proper terminology to discuss in detail.
Basically, colour theory is the fix of best practices for picking colors together for harmonious designs and contextual color combinations.
That is the idea that specific color schemes are more than appealing to the human eye and depend on the context.
Why Is It Then Important?
No matter what chapters you work with color in your daily life, having a working understanding of colour theory will always come in handy.
Color is vital to making a production recognizable and appealing in branding and marketing.
Information technology also sends an instant message about what your make identity is. If your branding is a lite, diffuse lavender, that sends a very unlike message than if your branding is all blackness.
Nosotros live in fast times, and the message must be transmitted instantly and finer. When you consider that xc% of the data sent to the brain is visual, color theory becomes essential to convey the right message (branding and marketing) and influence people (sales).
That's why color psychology (and the significant of each color) shouldn't be overlooked.
Merely as an entrepreneur, you tin can't just slap carmine on your packaging and expect information technology to work as well as information technology did for Coke. There'due south a lot more to information technology than that, which we'll get into.
Even if yous're non in sales or marketing, colour theory is however disquisitional. It'll make your art and design more effective and aid yous develop a better center for color.
And even if yous're not an artist, designer, or entrepreneur, knowing more about color volition help you talk well-nigh it competently in all areas of your life.
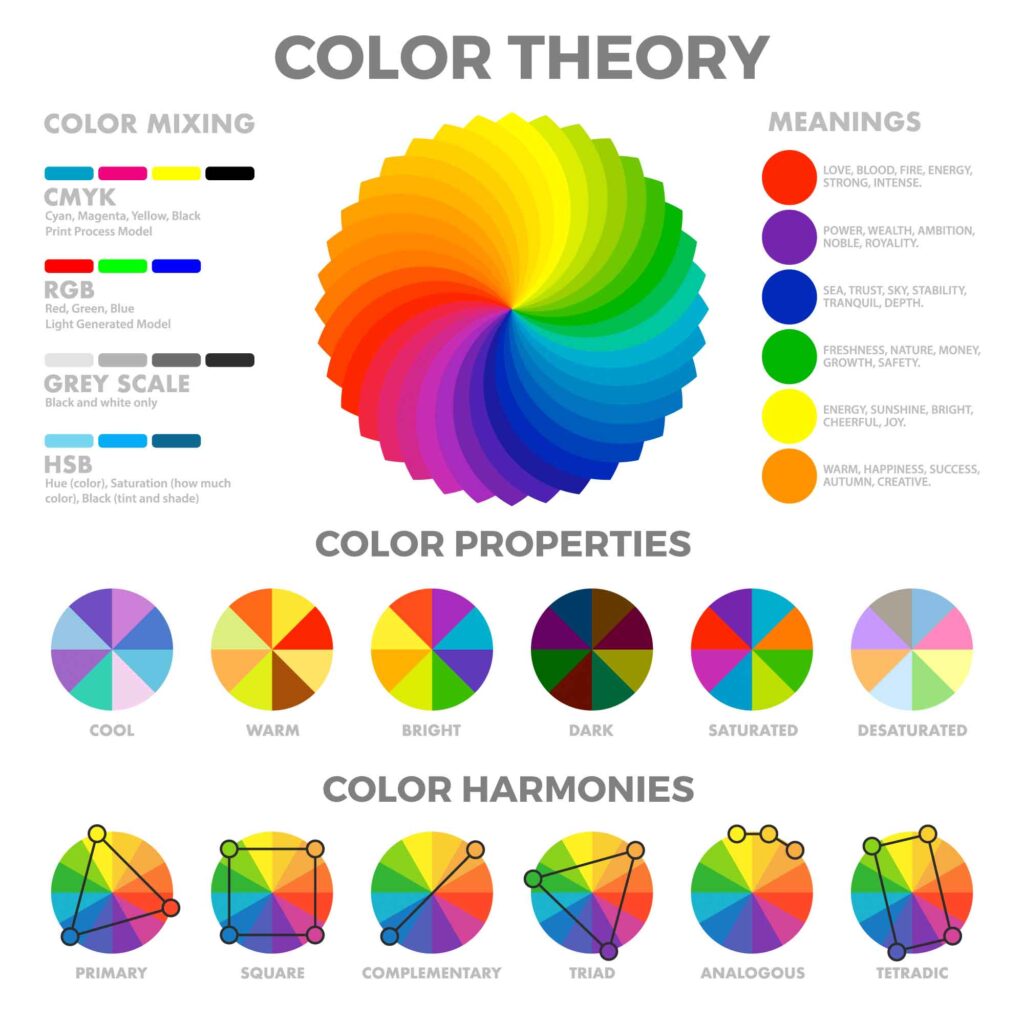
Color Models
At that place are three unlike colour models. Hither'south what you need to know well-nigh each of them.
RGB (Red, Green, Blueish)
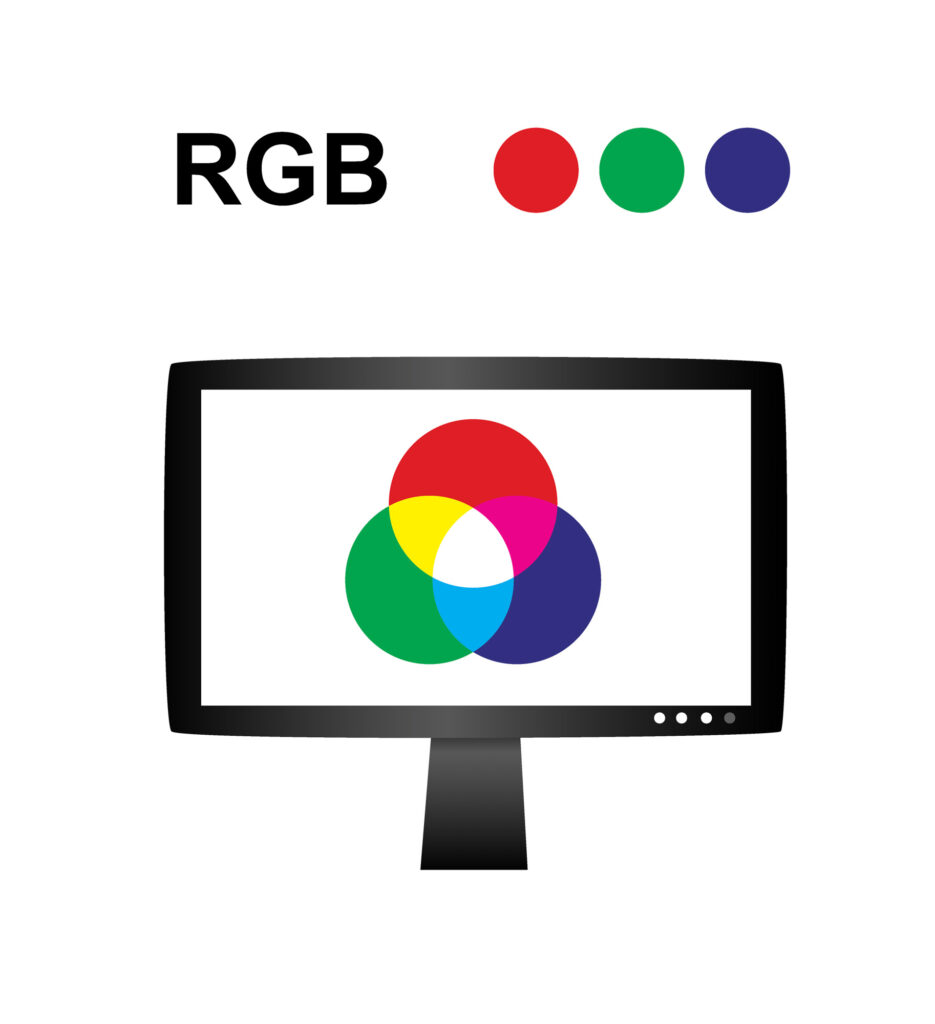

TVs, projectors, and electronics screens use the RGB model and ruby-red, green, and bluish equally their primary colors.
While the RYB model involves mixing pigments, the RGB model involves mixing light to create other colors.
This makes RGB an additive, rather than subtractive, color model. Instead of starting with white and subtracting color away from information technology, RGB begins with black and applies red, green, and bluish low-cal sources of varying intensities.
The more than light yous add together, the brighter the colour becomes. If yous mix all three colors of light in equal amounts, you'll become pure, white calorie-free.
CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Xanthous, and Key – or Black)
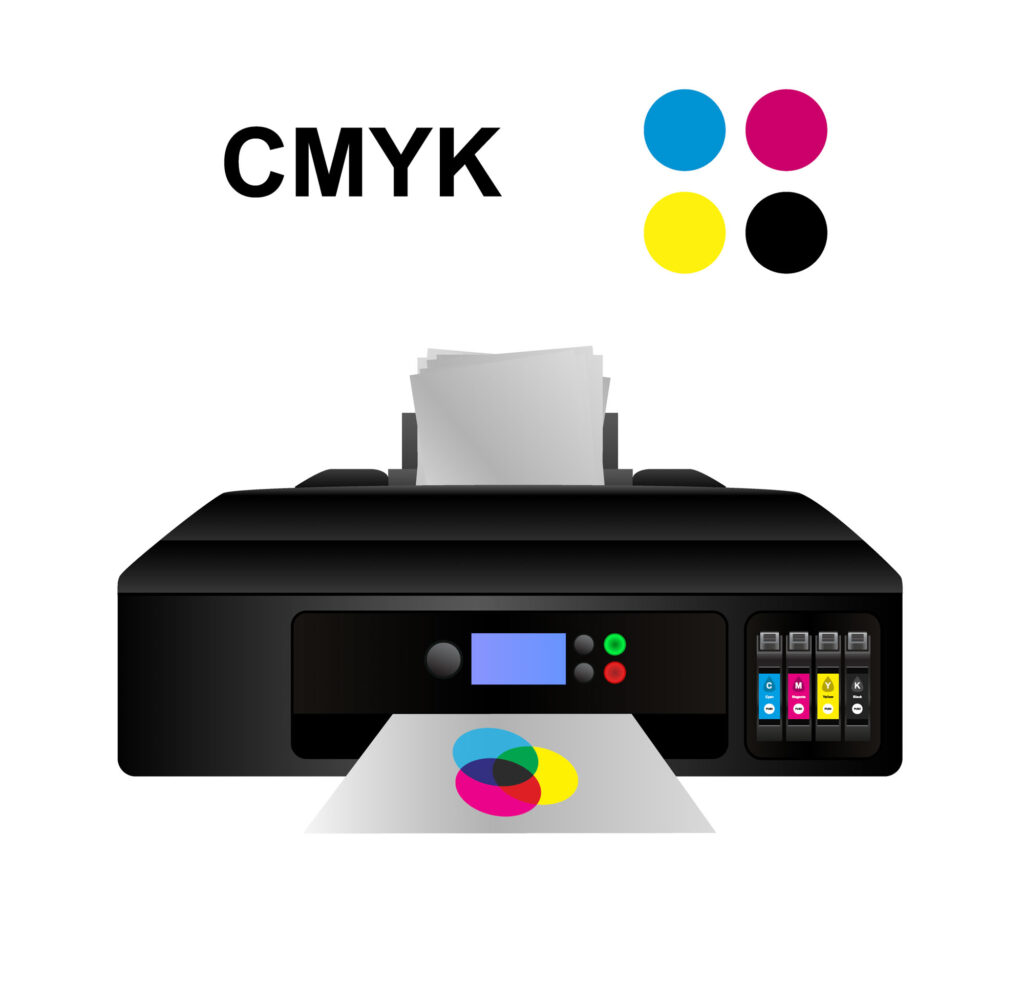

Any color you encounter on a physical printed surface uses the CMYK color model. This uses the same color wheel as the RGB model, but make no mistake – these are two dissimilar color models.
Dissimilar RGB, CMYK is a subtractive color mixing model. Colors are produced by subtracting light from newspaper by adding pigmented ink to a white surface.
And dissimilar RGB, CMYK uses different master colors because cyan, magenta, xanthous, and blackness allow printers produce a wider variety of colors on newspaper.
Continue in mind that although you'd use CMYK to create printed materials, if you used CMYK instead of RGB to post your logo on a screen, the color wouldn't look right when posted online or used on your website.
It'southward important to know when to switch betwixt the two models.
RYB (Red, Yellow, Blue)
This is the color model y'all probably learned as a child, mixing finger paints in school.
Today, it'southward known every bit "traditional" color theory and continues to be used past artists and designers to mix paints and create color palettes. The chief colors are red, yellow, and blue.
This is a subtractive colour mixing model. This means that y'all first with the white of a canvas or piece of paper, and so subtract the light reflected past the newspaper past adding pigment color (pigment, crayon, marker, etc.) to it.
Remember, white is a combination of every other color.
Color Bike Theory
Sir Isaac Newton mapped the color spectrum into a color circle in 1666. Today, nosotros call this circle color bicycle, which has 12 basic colors.
It organizes the iii primary colors, iii secondary colors, and six 3rd colors (or intermediate colors) into a slope wheel, showing their relation to one another in an easy-to-understand visual model.
Today, at that place are 3 colour wheels – one for each color model. But the relationships between the colors on the colour wheel remain the aforementioned, no matter which wheel you're using.
Artists and designers refer to the colour cycle when choosing color schemes for any project that involves color.
In order to understand how colors chronicle to one another, you need a firm agreement of the colour wheel.
Principal, Secondary, and Tertiary Colors
The color wheel is organized into primary, secondary, and tertiary colors.
Primary colors are the iii chief edifice blocks of the color cycle – the colors that can't be created by mixing other hues.
- Ruby-red
- Greenish
- Blueish
Secondary colors consist of two primary colors mixed in equal amounts.
- Reddish + blue = Magenta
- Dark-green + red = Yellow
- Blue + green = Cyan
Third colors are created by mixing secondary and primary colors to create new hues.
- Green + yellow = Chartreuse
- Green + cyan = Spring green
- Bluish + cyan = Azure
- Blueish + magenta = Violet
- Red + magenta = Rose
- Scarlet + yellow = Orangish
Why does this matter for colour theory? In order to take reward of the full globe of color, you need to be able to access the full spectrum of colour, and you can't do that without understanding how unlike hues are created.
Hue, Value, and Chroma

After mastering the color cycle, it's time to take the side by side step – learning about hue, value, and blush.
These are important terms to sympathise because they let us to talk more in-depth almost colors and color theory.
Hue
Hue is the pure form of any color, its position on the color bike. It refers to the color family as in ruby-red, blue, light-green. It'south what we usually mean when we employ the word "colour."
Value
Value refers to how pure the color is – whether it has shades, tints, or tones added to it to modify its advent. (We'll explain these concepts in the next department.)
Blush
Chroma refers to how pale or saturated a given colour is.
Shade, Tint, and Tone

Shade, tint, and tone create variations of hues on the color wheel.
They're essential to understanding color theory because, in the real globe, nosotros aren't simply working with mixing hues. Nosotros're also working on mixing hues with neutrals.
Shade
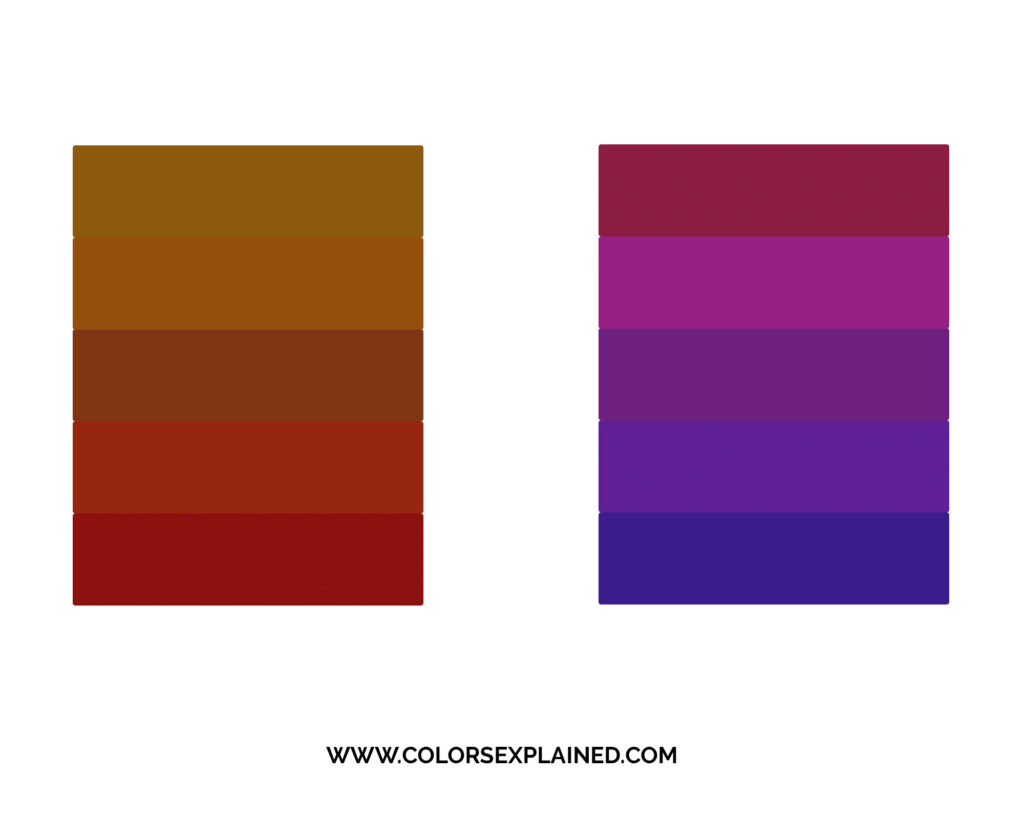
To create a shade of an existing color, add blackness to a given hue. For example, red and black make burgundy, a darker shade of ruby.
Tint
To create a tint of a detail color, add white to it.
Tone
To modify a color's tone, add gray. This darkens the original hue while making the color more subtle and less intense – more than diffuse and muted.
Color Temperature
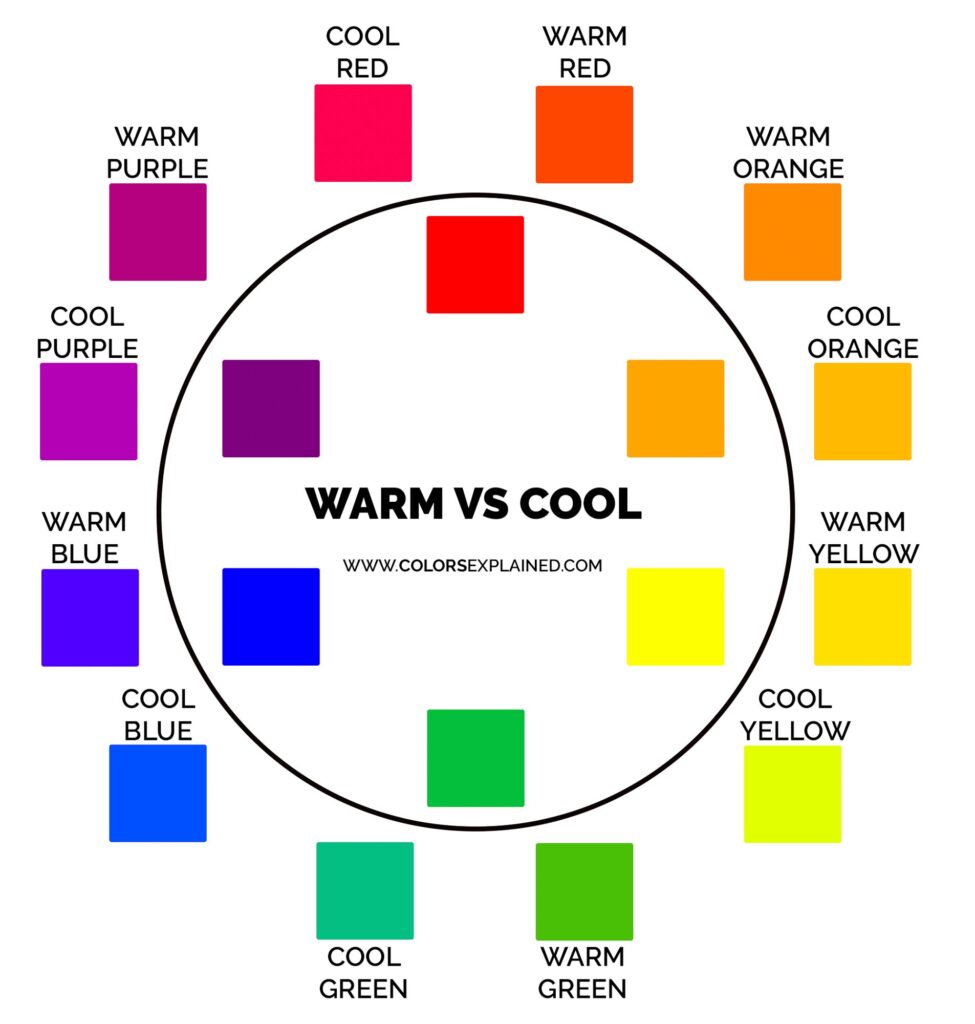
You can draw a straight line through the centre of the colour wheel and dissever the warm colors from the absurd colors.
As a quick dominion of thumb, reds, yellows, and oranges are warm colors, and dejection, greens, and purples are cool colors.
While this is a corking starting point, it's not quite that simple.
Every specific color has its own warm or absurd undertones. There are cool reds and warm greens, for instance.
So always pay attention to a color's undertones. The all-time way to larn to identify that is to practice!
Warm colors are usually associated with energy, effulgence, and activeness. Cool colors ordinarily instill calm, peace, and serenity.
Why does color temperature matter? Because our minds recognize it whether nosotros realize it or not.
Whether you're creating a work of art, designing the décor of a room, or choosing a color palette for your company logo, you want to factor in color temperature and how your selections will make people feel – consciously or subconsciously.
From principal colors upwardly until this point, nosotros've gone over categories and dimensions of color nowadays in an expanded color bike.
They create countless colour combinations, simply they won't get the task done unless they're arranged in harmonious color schemes. That'southward why you want to learn about color harmonies.
Color Harmony
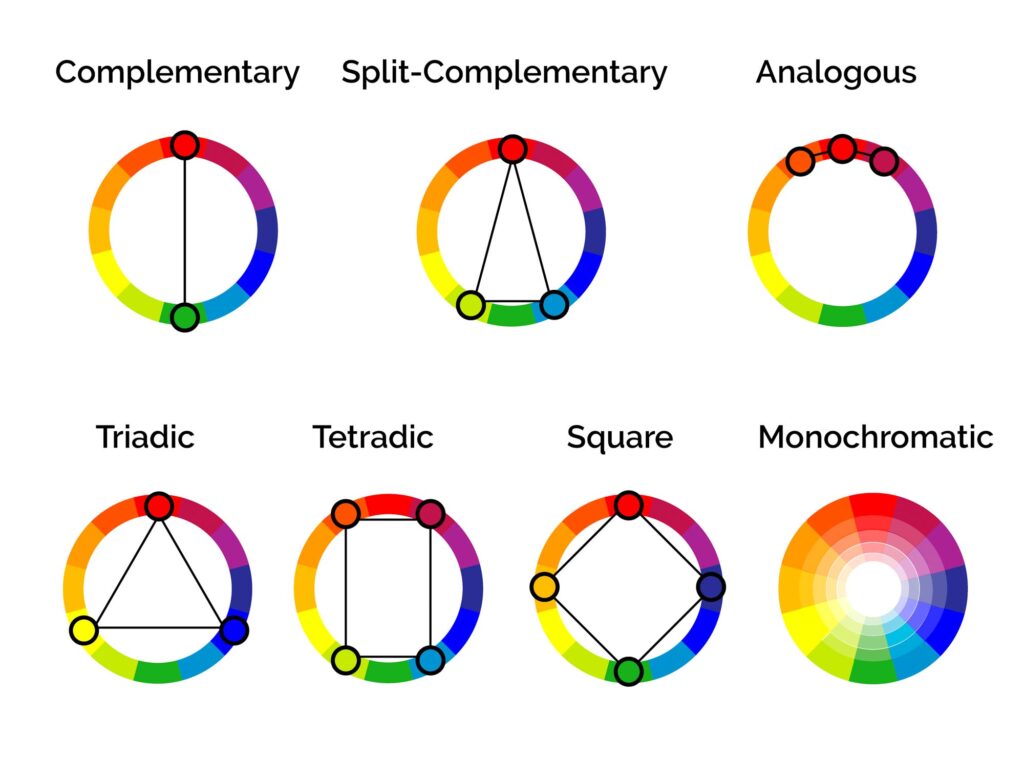
Color harmonies are color arrangements that are pleasing to the centre. They create a sense of cohesion. They're what makes a color scheme "piece of work."
This matters for colour theory because color doesn't exist in a vacuum; we experience colour within the context of the world—individual hues and tones playing confronting one some other.
When a color scheme isn't harmonious, it's either boring or chaotic. A lack of harmony can mean an over-stimulating design that's difficult to expect at.
Merely it can too be an experience that's so irksome and monotonous that the eye glazes right over it. Colour harmony is about finding the heart ground betwixt the 2 options.
This also matters considering when designing with user experience and accessibility issues (such as colour incomprehension) in mind, certain color harmonies and contrast levels are easier to read than others.
It'southward essential to maintain enough contrast for color blind people to be able to still see and capeesh your designs.
Here's a quick primer on the main color harmonies to get y'all started.
Monochromatic

The most straightforward color harmony, a monochromatic colour scheme includes a unmarried hue with varying shades and tints.
This produces a consistent look and feel and often ends up looking neat and polished.
It's as well the hardest color harmony to mess upwards. Merely it lacks colour contrast and can risk looking too dull or hard to read.
Complementary

A complementary color harmony uses 2 colors from opposite sides of the colour wheel, like red and green.
Having and so much precipitous contrast between the two colors can brand imagery pop, creating a blueprint that's very easy to read.
That's why then many logos use this color harmony. But overusing this much contrast can exist exhausting to look at.
Split-Complementary

A split-complementary harmony includes one dominant colour and the ii colors directly side by side to the dominant color's complement on the colour bike.
A divide-complementary scheme has more nuance than a complementary ane but all the same has the benefit of a lot of dissimilarity. However, this can make it harder to balance.
Coordinating

An analogous colour scheme uses colors direct adjacent to each other on the color wheel – for case, red, orangish, and yellowish.
Use the 60-30-x rule with this harmony – use the dominant color sixty% of the time, a supporting color xxx% of the time, and the 3rd accent color 10% of the fourth dimension.
An accent color can exist a great tool to depict the eye to of import components of the design.
This scheme is pleasing to the center and easy to expect at. It'southward also very effective in things like web blueprint.
Use the dominating and supporting colors to create a harmonious and varied website, then employ the accent color for activity items like "Buy Now" or "Contact Usa."
Triadic

Triadic colour schemes consist of iii colors evenly spaced around the color wheel.
This produces vivid and dynamic designs with plenty of contrast while even so feeling harmonious.
Each detail stands out, while the overall epitome pops and is easy to read.
Withal, a triadic scheme can wait juvenile and overwhelming if done incorrect. It takes an experienced designer to pull this off.
Try choosing one ascendant color and using the others sparingly, or choosing a softer tint of the other two colors (by adding gray).
Square

The foursquare scheme uses four colors, all equidistant on the colour wheel. Two complementary pairs. This creates a square or diamond shape on the colour cycle.
In addition, it also creates tons of contrast and gives y'all plenty of colors to play with.
Instead of using all four colors in equal amounts, choose ane dominant color and use the others for back up and accents.
Tetradic
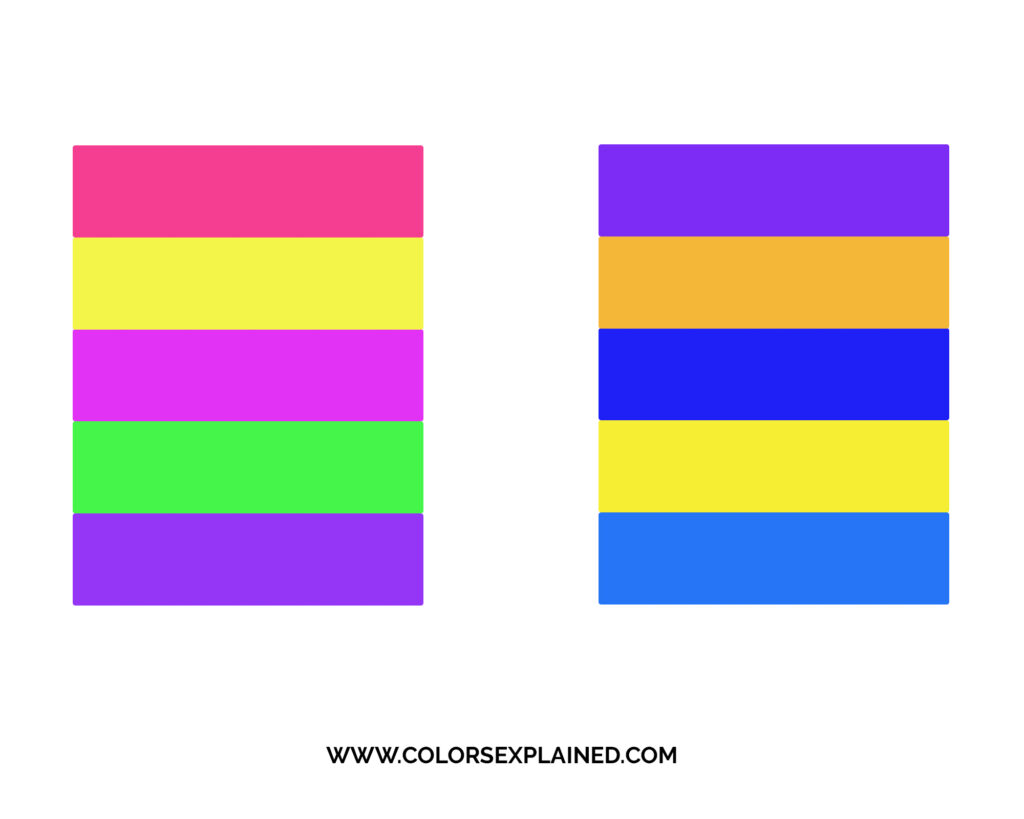
The tetradic color scheme is also called the rectangular color scheme considering of its shape on the color bicycle.
The benefits and palette are similar to the square color scheme, but considering each hue is closer to one another on the color wheel, they're organized into natural pairs.
The Significant of the Colors
Every bit we said in a higher place, color psychology is essential to convey the correct message and influence people.
However, different colors are perceived differently by distinct audiences around the world.
It's crucial to sympathise your audition to know what colors will convey your message best.
Ask yourself, "who is my audience?" Attempt to pivot down their gender, age, religion, and geographical location.
In add-on, cultural differences shouldn't be ignored since the psychological effects of a hue that'due south happy and uplifting in one state might exist depressing in another.
The answers to these questions volition give your pattern a jumpstart.

In addition, information technology's important to remember that color symbolism can exist instinctual, universal, and timeless. It's something that has been hardwired into u.s. since the dawn of humanity.
That's why nearly color meanings are based on nature (blue for serenity, green for growth, red for danger and warmth).
All the same, color symbolism can also be contemporary, and so its meanings will evolve with fourth dimension and personal experiences (mostly subconsciously). Afterwards all, our mural is very different from what our ancestors used to see.
Either way, hither are the meanings of the colors in general lines.
Just go on in mind that color symbolism is also influenced by a few other factors, such as the color itself, the color combination, its quantity in a given design, the shape the color occupies, and objects or imagery.
Cerise: passion, physical energy, warmth, aggression, and danger.
Yellow: happiness, creativity, mental stimulation, impatience, and cowardice.
Blue: calmness, honesty, trust, stability, and responsibility.
Orange: spontaneity, risk, dynamism, warmth, exhibitionism, and superficiality.
Light-green: growth, freshness, harmony, prosperity, enviousness, and greediness.
Imperial: spirituality, imagination, mystery, royalty, wisdom, and immaturity.
Pink: unconditional dear, sympathy, femininity, comfort, playfulness, and childishness.
Brown: strength, dependability, warmth, honesty, anticipated, and loneliness.
Blackness: power, elegance, mystery, formality, authorisation, fear, and pessimism.
White: purity, innocence, delicacy, cleanliness, coldness, and unfriendliness.
Gray: neutrality, wisdom, intellect, seriousness, boredom, and low.
How to Utilize Color Theory
Enough with the theory. Now permit's become to the practice.
You already know all the concepts and classifications, and then below, nosotros'll walk y'all through how to choose the best colors for your design.
Step 1: Sympathize Who Your Audience Is
Information technology's of import to understand colors, but you likewise need to consider how your audience volition react to them.
People take different color preferences based on their gender, historic period, geographic location, organized religion, and economic status. Make sure you know these aspects almost your audience.
Step back and make certain you expect at it from an outsider'south signal of view. Shift your focus from you to them.
Step 2: Set a Mood for Your Pattern
Consider the mood or feeling you lot want to attribute to your brand, website, or product.
Colors evoke emotional responses in people. In fact, people "determine" subconsciously whether or non they like a product in 90 seconds or less.
Lighter shades are peaceful, darker colors are more confident, muted colors are more sophisticated, and bright colors are more energetic.
Hardly e'er a projection will telephone call for the pure hues. We often utilize adjusted colors by changing shade, tint, tone, temperature, so on to reach ameliorate contrast and convey the right message.
Hither are some basic guidelines for picking the mood.
- Bright – energetic, powerful, exciting.
- Muted – restful, not stimulating, more sophisticated.
- Light – gentle, soft, comforting, peaceful.
- Dark – serious, intense, professional.

Step 3: Pick a Few Words (And Colors, Too)
To pick your make'south colors, you can start with the color that conveys the well-nigh vital feature of your brand.
From here, you can build it out with a couple of extra colors, accents, or just a monochromatic color palette.
So first, pick the main color, considering the meaning of the colors and your brand'south personality (how you want people to perceive it).
An splendid manner to practise that is to write down words that describe your business or design. How do you want people to run across it?
Your goal is to create psychological connections with your audience. That'southward why y'all shouldn't begin with choosing colors simply words. Y'all want people to relate and associate experiences with your brand.
Next, transform these words into colors. Play with the colour harmonies using the colors you chose and perchance add others you hadn't considered before. See how they work out together.
Is that something that resonates with your make naturally?
Each color harmony has pros and cons. Choosing the advisable one is key to conveying the right mood regardless of the project.
Trial and error to find the correct color palette.
80% of the Fortune 500 companies have two or fewer colors incorporated into their logo.
Step four: Consider the Color Context
Every bit important equally choosing the right colors, colour context volition influence how people perceive the hues you've chosen.
That'due south because colors appear differently when placed next to each other.
If you place a red button on top of an orangish background, it volition brand the ruby appear duller. But if you lot put the same ruby button on a turquoise or blue background, it will appear brighter.
Consider color context and contrast when using your fore and background colors so your design won't backfire. You might even realize you demand to change your color palette or utilise them differently.
In addition, this step is crucial for accessibility as y'all can assess if your design accommodates the needs of color-blind people.
Step five: Utilize the 60-30-10 Rule
Apply the chosen color palette using the lx-thirty-10 blueprint dominion. For that, utilise the dominant color 60% of the pattern, a supporting colour 30%, and the 3rd accent color x% of the fourth dimension.
These aren't hard-and-fast numbers, just they give a sense of proportion and residue and avert creating a childish and garish design.
Step half-dozen: Draft Numerous Designs
Now it's time to put everything you have chosen into your design. Typhoon multiple designs based on the colors and harmonies yous picked, wait a couple of days and check the designs with a clear caput once again.
In this footstep, you'll probably typhoon, review, and work on a new draft at least a few times, but that's okay! Remember, practice makes perfect.
Colour is an ever-evolving art form, and the more y'all play with color and practice design, the better yous go. No designer or artist creates their masterpiece the start time around.
Here are a few powerful tools to create your colour palette or find inspiration for any color choice.
Adobe Color – Color palette generator based on multiple harmonies. You also tin can extract the theme of a photo and check color contrast for accessibility.
Coolors – Our favorite color combination generator which multiple options to create cohesive color palettes. It allows yous to start with i color or a few colour choices and then establishes a scheme for you. If you don't like what you see, press the infinite bar on your keyboard, and the tool volition prompt y'all with a new color palette.
Canva – Excellent palette generator. You can upload images and go some cool color ideas based on a photo which colour scheme y'all like.
Color Terminology Glossary
Accent: Accent colors are boosted colors that generally contrast or complement the other colors used in a design.
Additive color model: The additive color model describes how light produces color.
Coordinating: Analogous colors are next to each other on the color bicycle.
Chroma: The quality of purity, intensity, or saturation of a given color.
Complementary: Two colors that are on opposite sides of the colour wheel.
Hue: Hue is a pure pigment—i without tint or shade (added white or black paint, respectively).
Intermediate: A colour created by mixing a primary colour with the secondary color next to it in the RYB colour model. Likewise called a tertiary color in the RGB colour model.
Monochromatic: A palette containing or using only one color, one hue.
Neutral: Neutral colors are muted shades that lack color but often take underlying hues that change with unlike lighting.
Saturation: Color saturation refers to the intensity of color in an prototype. Every bit the saturation increases, the colors appear to be purer.
Secondary: These are color combinations created by the equal mixture of 2 primary colors.
Shade: Shade is a hue or mixture of pure colors to which only black is added.
Subtractive color model: In the subtractive color model, pigment is used to produce colour using reflected calorie-free.
Primary: Colors or colored lights that tin can be mixed in varying amounts to produce a gamut of colors.
Split up-Complementary: A dissever-complementary colour scheme takes up a base color and ii secondary colors.
Triadic: A triadic colour scheme comprises three colors evenly spaced on the color wheel.
3rd: The combination of principal and secondary colors is known as 3rd in the RGB color model, and the combination of two secondary colors is known equally tertiary in the RYB colour model.
Tint: Tint refers to whatever hue or mixture of pure colors to which white is added.
Tone: Tones are created when grey is added to a color.
Undertone: It refers to a subdued or muted tone of colour.
Value: Value refers to the lightness or darkness of a colour.
Wavelength: Wavelength is the spatial menstruum of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. It is the altitude betwixt consecutive respective points of the same phase on the moving ridge. The range of wavelengths or frequencies for moving ridge phenomena is chosen a spectrum.
Final Thoughts on Color Theory 101
We hope you tin employ the principles of colour theory to create original and creative designs.
Understanding color theory is the first step to opening a world of possibilities and working with the rainbow of colors.
Whether you're working on an interior or graphic pattern project, color theory still applies. Besides, you lot will always desire a harmonic and centre-pleasing color scheme to convey your message.
Feel gratuitous to scan this site to deepen your report of colour.
Did you savour reading about colour theory? Then delight share this article with a co-worker or friend!
Source: https://www.colorsexplained.com/color-theory/
0 Response to "Art Must Be Able to Convey a Message Theory Name"
Post a Comment